|
| |||
|---|---|---|---|

|
|
||
VMM CHANNEL
The channel is the interface mechanism used by transactors to transfer transactions. Transaction objects are produced or consumed by a transactor. Transactor can be a generator or a driver or a scoreboard. In Transaction-level modeling multiple processes communicate with each other by sending transactions through channels. For example, to transfer a transaction from generator to a driver, we don't need to send at signal level. To transfer a transaction from Driver to DUT, physical signals are used. The channel transfers transactions between the verification components, and it serves as a synchronizing agent between them.
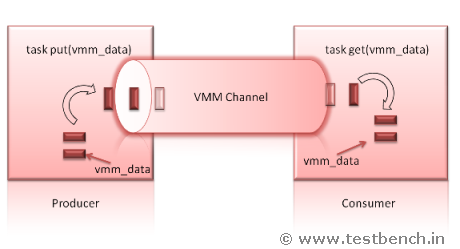
Channels are similar to SystemVerilog mailboxes with advanced features. Vmm Channels provides much richer feature functionality than a SV mailbox. vmm channels are superset of mailboxs.
Some of the the benefits of channels over mailboxes:
 Dynamic reconfiguration
Dynamic reconfiguration
 Inbuilt notifications
Inbuilt notifications
 Strict type checking
Strict type checking
 Out of order usage
Out of order usage
 task tee() for easy scoreboarding
task tee() for easy scoreboarding
 Record and playback
Record and playback
 task sneak() for monitors
task sneak() for monitors
Using `vmm_channel() macro , channels can be created.
`vmm_channel(Custom_vmm_data)
The above macro creates a channel Custom_vmm_data_channel . There are various methods to access the channels.
In the following example, we will see
1) Channel creation using macros.
2) Constructing a channel.
3) Pushing a transaction in to channel.
4) Popping out a transaction from the channel.
We will create a channel for vmm_data for this example. Users can create a channel for any transaction which is derived from the vmm_data class. You can try this example by creating channel for Packet class which is discussed in previous section.
1) Define a channel using macro
`vmm_channel(vmm_data)
2) Construct an object of channel which is defined by the above macro.
vmm_data_channel p_c = new("p_c","chan",10);
3) Push a packet p_put in to p_c channel.
p_c.put(p_put);
4) Get a packet from p_c channel.
p_c.get(p_put);
Complete Example
`vmm_channel(vmm_data)
program test_channel();
vmm_data p_put,p_get;
vmm_data_channel p_c = new("p_c","chan",10);
int i;
initial
repeat(10)
begin
#( $urandom()%10);
p_put = new(null);
p_put.stream_id = i++;
$display(" Pushed a packet in to channel with id %d",p_put.stream_id);
p_c.put(p_put); // Pushing a transaction in to channel
end
initial
forever
begin
p_c.get(p_get); // popping a transaction from channel.
$display(" Popped a packet from channel with id %d",p_get.stream_id);
end
endprogram
(S) Download the file
vmm_channel.tar
Browse the code in vmm_channel.tar
(S) Command to run the simulation
vcs -sverilog -f filelist -R -ntb_opts rvm -ntb_opts dtm
(S) Log report
Pushed a packet in to channel with id 0
Popped a packet from channel with id 0
Pushed a packet in to channel with id 1
Popped a packet from channel with id 1
Pushed a packet in to channel with id 2
Popped a packet from channel with id 2
Pushed a packet in to channel with id 3
Popped a packet from channel with id 3
Pushed a packet in to channel with id 4
Popped a packet from channel with id 4
Pushed a packet in to channel with id 5
Popped a packet from channel with id 5
Pushed a packet in to channel with id 6
Popped a packet from channel with id 6
Pushed a packet in to channel with id 7
Popped a packet from channel with id 7
Pushed a packet in to channel with id 8
Popped a packet from channel with id 8
Pushed a packet in to channel with id 9
Popped a packet from channel with id 9
Vmm Channel Methods.
function new ( string name, string instance,
int unsigned full = 1, int unsigned empty = 0, bit fill_as_bytes = 0 );
function void reconfigure (int full = -1, int empty = -1, logic fill_as_bytes = 1'bx );
function int unsigned full_level ( );
function int unsigned empty_level ( );
function int unsigned level ( );
function int unsigned size ( );
function bit is_full ( );
function void flush ( );
function void sink ( );
function void flow ( );
function void lock ( bit [1:0] who );
function void unlock ( bit [1:0] who );
function bit is_locked ( bit [1:0] who );
task put ( class_name obj, int offset = -1 );
function void sneak ( class_name obj, int offset = -1 );
function class_name unput ( int offset = -1 );
task get ( output class_name obj, input int offset = 0 );
task peek ( output class_name obj, input int offset = 0 );
task activate ( output class_name obj, input int offset = 0 );
function class_name active_slot ( );
function class_name start ( );
function class_name complete ( vmm_data status = null );
function class_name remove ( );
function active_status_e status ( );
task tee ( output class_name obj );
function bit tee_mode ( bit is_on );
function void connect ( vmm_channel downstream );
function class_name for_each ( bit reset = 0 );
function int unsigned for_each_offset ( );
function bit record ( string filename );
task bit playback ( output bit success, input string filename,
input vmm_data loader, input bit metered = 0 );
Refer to VMM book for details of each method.
The channel is the interface mechanism used by transactors to transfer transactions. Transaction objects are produced or consumed by a transactor. Transactor can be a generator or a driver or a scoreboard. In Transaction-level modeling multiple processes communicate with each other by sending transactions through channels. For example, to transfer a transaction from generator to a driver, we don't need to send at signal level. To transfer a transaction from Driver to DUT, physical signals are used. The channel transfers transactions between the verification components, and it serves as a synchronizing agent between them.
Channels are similar to SystemVerilog mailboxes with advanced features. Vmm Channels provides much richer feature functionality than a SV mailbox. vmm channels are superset of mailboxs.
Some of the the benefits of channels over mailboxes:
Using `vmm_channel() macro , channels can be created.
`vmm_channel(Custom_vmm_data)
The above macro creates a channel Custom_vmm_data_channel . There are various methods to access the channels.
In the following example, we will see
1) Channel creation using macros.
2) Constructing a channel.
3) Pushing a transaction in to channel.
4) Popping out a transaction from the channel.
We will create a channel for vmm_data for this example. Users can create a channel for any transaction which is derived from the vmm_data class. You can try this example by creating channel for Packet class which is discussed in previous section.
1) Define a channel using macro
`vmm_channel(vmm_data)
2) Construct an object of channel which is defined by the above macro.
vmm_data_channel p_c = new("p_c","chan",10);
3) Push a packet p_put in to p_c channel.
p_c.put(p_put);
4) Get a packet from p_c channel.
p_c.get(p_put);
Complete Example
`vmm_channel(vmm_data)
program test_channel();
vmm_data p_put,p_get;
vmm_data_channel p_c = new("p_c","chan",10);
int i;
initial
repeat(10)
begin
#( $urandom()%10);
p_put = new(null);
p_put.stream_id = i++;
$display(" Pushed a packet in to channel with id %d",p_put.stream_id);
p_c.put(p_put); // Pushing a transaction in to channel
end
initial
forever
begin
p_c.get(p_get); // popping a transaction from channel.
$display(" Popped a packet from channel with id %d",p_get.stream_id);
end
endprogram
(S) Download the file
vmm_channel.tar
Browse the code in vmm_channel.tar
(S) Command to run the simulation
vcs -sverilog -f filelist -R -ntb_opts rvm -ntb_opts dtm
(S) Log report
Pushed a packet in to channel with id 0
Popped a packet from channel with id 0
Pushed a packet in to channel with id 1
Popped a packet from channel with id 1
Pushed a packet in to channel with id 2
Popped a packet from channel with id 2
Pushed a packet in to channel with id 3
Popped a packet from channel with id 3
Pushed a packet in to channel with id 4
Popped a packet from channel with id 4
Pushed a packet in to channel with id 5
Popped a packet from channel with id 5
Pushed a packet in to channel with id 6
Popped a packet from channel with id 6
Pushed a packet in to channel with id 7
Popped a packet from channel with id 7
Pushed a packet in to channel with id 8
Popped a packet from channel with id 8
Pushed a packet in to channel with id 9
Popped a packet from channel with id 9
Vmm Channel Methods.
function new ( string name, string instance,
int unsigned full = 1, int unsigned empty = 0, bit fill_as_bytes = 0 );
function void reconfigure (int full = -1, int empty = -1, logic fill_as_bytes = 1'bx );
function int unsigned full_level ( );
function int unsigned empty_level ( );
function int unsigned level ( );
function int unsigned size ( );
function bit is_full ( );
function void flush ( );
function void sink ( );
function void flow ( );
function void lock ( bit [1:0] who );
function void unlock ( bit [1:0] who );
function bit is_locked ( bit [1:0] who );
task put ( class_name obj, int offset = -1 );
function void sneak ( class_name obj, int offset = -1 );
function class_name unput ( int offset = -1 );
task get ( output class_name obj, input int offset = 0 );
task peek ( output class_name obj, input int offset = 0 );
task activate ( output class_name obj, input int offset = 0 );
function class_name active_slot ( );
function class_name start ( );
function class_name complete ( vmm_data status = null );
function class_name remove ( );
function active_status_e status ( );
task tee ( output class_name obj );
function bit tee_mode ( bit is_on );
function void connect ( vmm_channel downstream );
function class_name for_each ( bit reset = 0 );
function int unsigned for_each_offset ( );
function bit record ( string filename );
task bit playback ( output bit success, input string filename,
input vmm_data loader, input bit metered = 0 );
Refer to VMM book for details of each method.
Index
Introduction
Vmm Log
Vmm Env
Vmm Data
Vmm Channel
Vmm Atomic Generator
Vmm Xactor
Vmm Callback
Vmm Test
Vmm Channel Record And Playback
Vmm Scenario Generator
Vmm Opts
Report a Bug or Comment on This section - Your input is what keeps Testbench.in improving with time!

Introduction
Vmm Log
Vmm Env
Vmm Data
Vmm Channel
Vmm Atomic Generator
Vmm Xactor
Vmm Callback
Vmm Test
Vmm Channel Record And Playback
Vmm Scenario Generator
Vmm Opts
Report a Bug or Comment on This section - Your input is what keeps Testbench.in improving with time!

